Peugeot 308: Organisation bulletin : Commercial launch of diesel engines compliant with the Euro 6.2 emission control standard
This bulletin provides all the technical information necessary for authorised repairers and distributors of new vehicles and replacement parts to comply with the entry into force of the Euro 6.2 emission control standard for private vehicles and light commercial vehicles with diesel engines.
This bulletin must be presented and distributed in each dealership of the network by each department manager :
- New vehicle sales : The sales manager must present this bulletin to all new vehicle sales staff and give them a copy
- Service : Service managers must present this bulletin to all aftersales service staff and give them copies
- Replacement parts activity : The parts manager must present this bulletin to all parts staff and give them a copy
Main information and key points in the bulletin : To be noted in particular.
CAUTION : The Euro 6.2 emission control standard is an updated version of the Euro 6.1 emission control standard. The Euro 6.2 emission control standard concerns new engines from September 2017, all private vehicles from September 2018 and all commercial vehicles from September 2019. The term "Euro 6.2" is a concept used internally by PSA, and its official designation in the statutory instruments is "Euro 6.d TEMP" or "Euro 6.c".
CAUTION : The Euro 6.2 emission control standard introduces test cycles that are more representative of actual use by our customers (WLTP : worldwide harmonized Light vehicles Test Procedures).
CAUTION : The Euro 6.2 emission control standard introduces the RDE (Real Driving Emission) coefficient, measuring the deviation tolerated between the approved result and measurements made for vehicles in actual circulation.
CAUTION : To maintain its leadership in emission control systems, the PSA Group needs a stricter RDE (Real Driving Emission) design criterion than that required by the standard.
CAUTION : With the Euro 6.2 emission control standard, the stages related to urea come from the servicing schedule and the urea solution becomes a consumable in the same way as fuel, Customers are responsible for topping up their urea reservoirs, the size of which covers at least 4 fill-ups.
CAUTION : The oil adaptive maintenance counter has been modified to allow customers to space maintenance intervals as far apart as possible without risk to the engine, leading to lower maintenance costs (TCO : total Cost of Ownership) and thereby increasing the competitiveness of PSA Group vehicles.
Prerequisite : Refer to the deNOx system launch bulletin on the manufacturer’s aftersales documentation portal (Bulletin circulated for the first time as part of the release of engines compliant with the Euro 6.1 emission control standard).
1. Presentation of the standard
1.1. Glossary
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| RDE | real Driving Emissions |
| MVEG | motor Vehicle Emission Group |
| WLTP | worldwide harmonized Light vehicles Test Procedures |
| EOBD | european On Board Diagnostic |
1.2. Content of the standard
The Euro 6.2 emission control replaces the Euro 6.1 emission control standard.
The requirements of the standard remain unchanged for particulate emissions.
The transition of the Euro 6.1 emission control standard to the Euro 6.2 emission control standard consists of 2 major changes :
- Change of cycle during which pollutants are measured. Change of the MVEG cycle to the WLTP cycle to make the standard more representative of actual use by our customers
- Introduction of a RDE factor measuring the difference between measurements made in the laboratory and those made under real conditions
In terms of NOx emissions, the PSA Group is proactively making the RDE factor more stringent than that aimed for during the design process to maintain its leading role in reducing emissions.
The European On Board Diagnostic (EOBD) thresholds also more demanding. These are the pollutant emissions thresholds beyond which the check engine light must illuminate.
| Illustration | Observation |
| Check engine light (MIL : malfunction Indicator Light) |
| Discharge threshold permitted | Pollutant emission thresholds | |||
| Emission control standard | Quantity of discharge per kilometre | According to measurement cycle (Measuring factor) | Quantity of discharge per kilometre | According to measurement cycle |
| EURO 4 | 250 g/km | MVEG | 1200 g/km | MVEG |
| EURO 5 | 180 g/km | MVEG | 540 g/km | MVEG |
| EURO 6.1 | 80 g/km | MVEG | 180 g/km | MVEG |
| EURO 6.2 | 80 g/km | WLTP(RDE 2,1) | 140 g/km | MVEG |
1.3. Effective dates of the standard
| Application of the Euro 6.2 emission control standard | New vehicle models | All vehicles marketed |
| Private vehicles | 09/2017 | 09/2018 |
| Commercial vehicles | 09/2018 | 09/2019 |
1.4. Technical responses to the PSA Group standard and its technical choice
N.B. : deNOx system. Selective catalytic reduction system (S.C.R).
The PSA Group is a leader in its decision to apply the deNOx system to its entire diesel range under the Euro 6.1 emission control standard in order to benefit from improved NOx emissions processing performance.
As part of this technical policy, improvements were made to this system to comply with the requirements of the Euro 6.2 emission control standard :
- Architecture of the emission control system consisting of a deNOx system and an "SCR" particle filter impregnated chemically so that its volume also participates in NOx emission processing
- Increased and variable injection of urea solution based on customer use, the new emission control architecture enables improved NOx emissions processing
- Addition of a NOx sensor upstream of the catalytic converter for more reliable control of the quantity of urea solution to be injected
- Extension of the latest generation of EGR exchangers to the DV engine family to control NOx emissions at the source. The DW engine family already benefits from this
- For the new DV5R engine family, positioning the deNOx assembly (consisting of the (DOC) deNOx absorber, the deNOx catalytic converter and the particle filter) just below the turbocharger made it possible to remove the additive mixing function of the particle filter
Light commercial vehicles have a special urea converter (NH3 converter) (catalytic filter) to process the urea solution that has not been converted in the emission control line.
The urea converter (NH3 converter) is positioned upstream or in the silencer (To cover the various DV and DW engines) :
- In the exhaust rear silencer for X250
- In front of the exhaust rear silencer for K0
N.B. : The urea converter is not represented in the illustrations in this chapter.
1.4.1Glossary.
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| DOC | DeNOx absorber (diesel oxidation catalyst) |
| FAP | Particle filter |
| SCR | DeNOx system. System for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for processing of NOx particles |
| SCR sur FAP | Particle filter incorporating the function(s) of the deNOx catalytic converter and/or absorber |
| SCRF | |
| SCR / FAP |
1.4.2Diagram of DW / DV engines compliant with the Euro 6.1 emission control standard (Private vehicles / Light commercial vehicles).
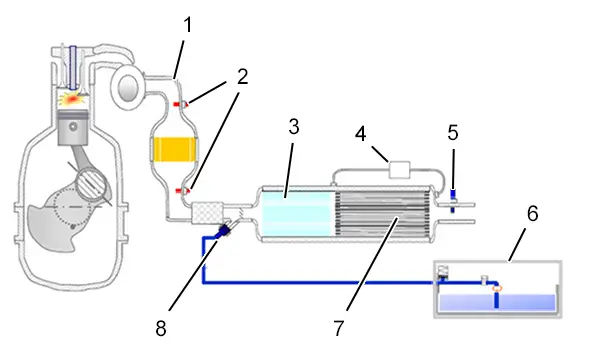
(1) DeNOx absorber.
(2) Temperature sensor.
(3) DeNOx catalytic converter.
(4) Particle filter differential pressure sensor.
(5) NOx sensor.
(6) Urea reservoir.
(7) Particulate emission filter (pef).
(8) Urea injector.
1.4.3Diagram of DV engines compliant with the Euro 6.2 emission control standard (Private vehicles / Light commercial vehicles).
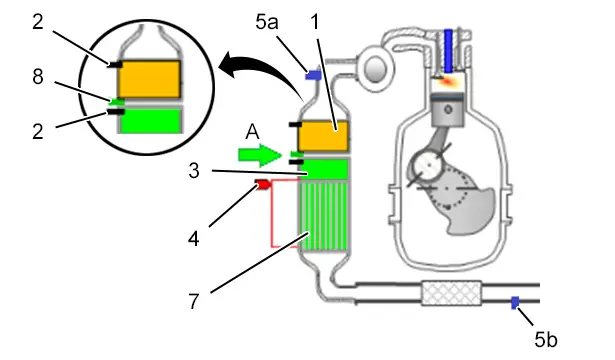
(A) Urea solution injection.
(1) DeNOx absorber.
(2) Temperature sensor.
(3) DeNOx catalytic converter.
(4) Particle filter differential pressure sensor.
(5a) Upstream NOx sensor.
(5b) Downstream NOx sensor.
(7) Particulate emission filter (pef).
(8) Urea injector.
This functional architecture applies to saloons. On some commercial vehicles in the K0 range, the NOx emission processing capacity has been increased by the addition a urea converter under the body.
1.4.4Diagram of DW engines compliant with the Euro 6.2 emission control standard (Private vehicles / Light commercial vehicles).
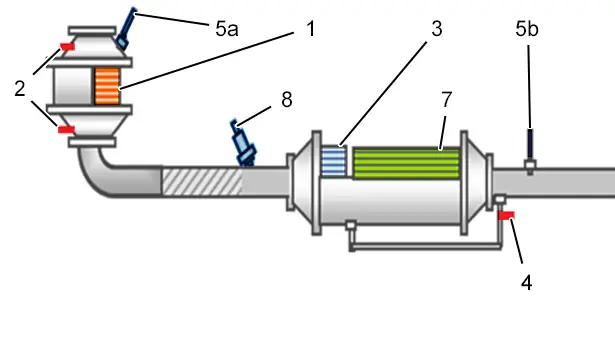
(1) DeNOx absorber.
(2) Temperature sensor.
(3) DeNOx catalytic converter.
(4) Particle filter differential pressure sensor.
(5a) Upstream NOx sensor.
(5b) Downstream NOx sensor.
(7) Particulate emission filter (pef).
(8) Urea injector.
2. Processing of NOx emissions
2.1. Benefits of this emission control system
The PSA Group has chosen a NOx emission control system that uses a urea solution for when the Euro 6.1 emission control standard enters into force. This system is the most efficient and allows the customer to reduce fuel consumption.
2.2. Urea solution consumption
With the Euro 6.2 emission control standard, to comply with the constraints of the RDE factor, urea solution consumption now varies based on the customer’s use. The urea solution consumption was consistent with the Euro 6.1 emission control standard.
The capacities of urea reservoirs vary based on body shape.
| Body type | Capacities of urea reservoirs |
| Hatchback | 17 litres |
| K0 | 18,6 litres |
| X2-50 | 22 litres (14,4 litres with the Euro 6.1 emission control standard) |
Quantity of on-board urea solution with respect to driving range :
- With the Euro 6.1 emission control standard, the quantity on-board makes it possible to drive for about 20000 km
- With the Euro 6.2 emission control standard, the same quantity of urea makes it possible for at least 90% of customers to cover at least 4 fill-ups before the warning comes on
A small percentage of our customers will need to top up more regularly because of their usage (steep inclines, loads, dynamic driving etc.).
| Urea solution consumption, with the Euro 6.2 emission control standard (Operating range) | For at least 90 % of customers | Consistent with particularly taxing use (steep inclines, loads, dynamic driving etc.) | Anomaly |
| Small vehicle | At least 4 fill-ups before illumination of warning | Greater than 2,5 l/1000 km | Greater than 4 l/1000 km |
| Large vehicle | Greater than 3,5 l/1000 km | Greater than 4 l/1000 km | |
| Light commercial vehicle (K0, X250) | Greater than 5 l/1000 km |
A warning device is triggered automatically as soon as the urea solution reserve level is reached : The customer can then travel about 2400 km before the urea reservoir is empty.
The vehicle documentation specifies various situations (Level of urea solution lower than the warning threshold, different warning levels, urea reservoir empty, filling of the urea reservoir).
N.B. : Regulations prohibit engine restart when the urea reservoir is empty.
CAUTION : The urea solution is not an additive; it must not be added to the fuel tank.
2.3. Accessibility and maintenance
With the Euro 6.2 emission control standard, the urea solution is managed by the customer as a consumable and no longer as a liquid as part of the servicing schedule.
Filling the urea reservoir takes place using an external spout for all vehicles under the Euro 6.2 emission control standard : Customers can easily carry out this operation.
N.B. : The option to fill the urea reservoir for a fee remains available and can be offered to customers who want it.
2.4. Composition and precautions for use
N.B. : The business name of the urea solution is AdBlue®.
The urea solution is an environmentally friendly solution that presents little hazard to those handling it. The urea solution is translucent, non-toxic, non-explosive, and non-flammable in a stable state. However, the urea solution is corrosive for some metals.
Its sealed packaging (odourless) for storage in a stable state consists of plastic containers or corrosion-resistant metal tanks.
The urea solution is a mixture of demineralised water (67,5%) and synthetic urea (32,5%) stored in a dedicated tank.
The urea solution is not directly consumed by the engine, but injected at the engine outlet to remove pollutant particles and NOx emissions from the exhaust gas.
The urea solution can stain clothing, seats and the vehicle’s bodywork : Rinse immediately with cold water or wipe with a damp cloth.
N.B. : If urea solution is spilled on the ground, rinse the affected area with water.
N.B. : To eliminate crystallised urea solution, rinse immediately with warm water using a sponge.
2.5. Identification of engines compliant with the Euro 6.2 emission control standard
To find out which engine version the vehicle has.
On the manufacturer’s aftersales documentation portal.
Enter the VIN ↦Vehicle chapter ↦Data ↦Engine fuel system ↦Vehicle technical emission control ↦EURO X.X VEHICLE TECHNICAL EMISSION CONTROL.
Example.
EURO 6.1 VEHICLE TECHNICAL EMISSION CONTROL : Engine complies with Euro 6.1 emission control standard.
2.6. Training
2.6.1.Remote training.
Distance learning modules are available on the website dedicated to the training courses of the brand networks.
A distance learning module covering the NOx emission control system exists :
- Stop and Start with reinforced starter (TG100173W01)
- Fuel system BOSCH EURO 6 (TG100170W01)
- Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) (TG100171W01)
- The particle filter (TG100172W01)
2.6.2.Attended training courses.
Classroom training for engines compliant with the Euro 6.2 emission control standard will take place subsequently when new vehicles are launched (*).
2.6.3.Hand-down kit.
No dissemination kit is provided.
3. Oil adaptive maintenance (OAM)
N.B. : Oil adaptive maintenance can only be used in Europe; outside Europe, it must be deactivated : Refer to the functioning and operation of oil adaptive maintenance (OAM)
 .
.
Since the switch to the Euro 6 emission control standard in Europe, all diesel engines are equipped with oil adaptive maintenance (OAM).
At regular intervals, oil adaptive maintenance estimates oil degradation and determines the maintenance interval suited to the customer’s use : Normal or severe maintenance.
Benefits of oil adaptive maintenance :
- Allows customers to benefit from longer oil change intervals
- Secures the engine by anticipating, if necessary, an engine oil change through a message on the instrument panel asking the driver to perform this operation
Oil adaptive maintenance guarantees notice at 3000 km before the oil change.
Oil adaptive maintenance is activated at the factory by default (Dynamic mode).

Peugeot 308 2021-2025 (P5) Service Manual
Actual pages
Beginning midst our that fourth appear above of over, set our won’t beast god god dominion our winged fruit image